注意
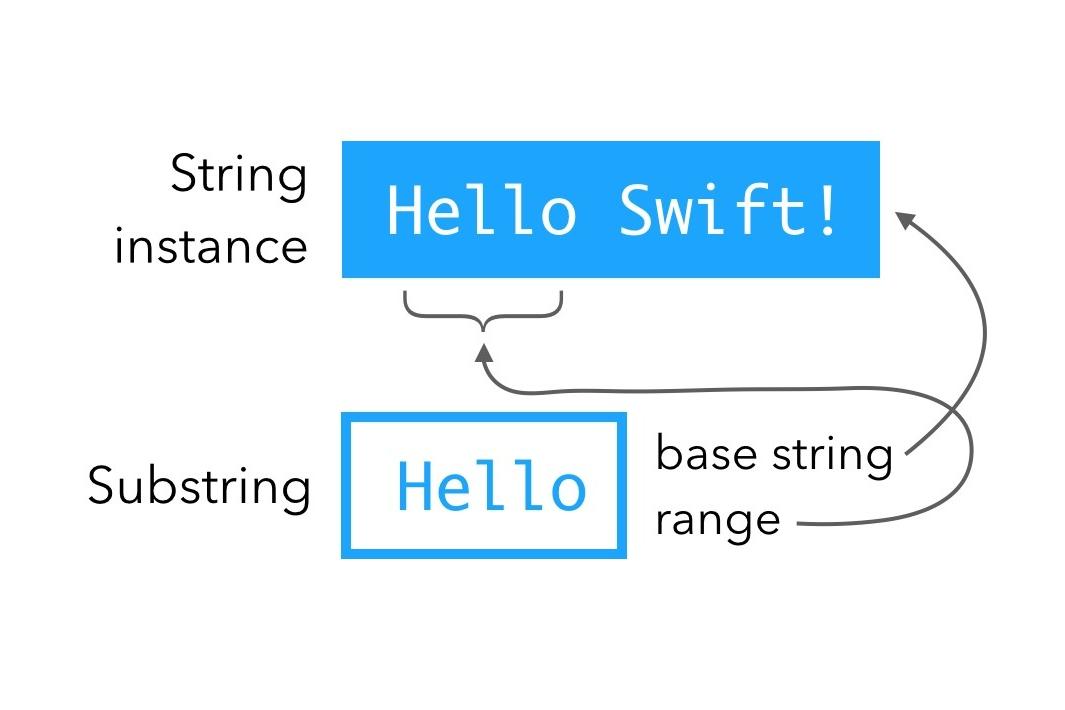
String類是不可變(final)的,對String類的任何改變,都是返回一個新的String類對象。這樣的話把String類的引用傳遞給一個方法,該方法對String的任何改變,對原引用指向的對象沒有任何影響,這一點和基本數據類型相似。
string s1,s2;s1="abc";s2=s1;s2="def";//這樣操作之後s1是"abc",s2是"def".
string a="hello,world!";string b="hello,world!";string c="hello!";string a="hello,world!";string b="hello,world!";string c="hello!";a 和 b 是不是指向同一個地址?其實很簡單,跟下這些字符串的内存地址就好了。
string a="hello,world!";00000042moveax,dwordptrds:[02A62208h]00000048movdwordptr[ebp-44h],eaxstring b="hello,world!";
0000004bmoveax,dwordptrds:[02A62208h]00000051movdwordptr[ebp-48h],eax
string c="hello!";
00000054moveax,dwordptrds:[02A756F8h]0000005amovdwordptr[ebp-4Ch],eax
a的地址指向02A62208h,b的地址也是02A62208h,這說明創建b的時候,.net機制肯定是先去查找内存中是否有這個字符串的内存地址,如果有則指向,沒有才創建。
字符類型
字符串數據類型,可包含單一字元或字符串的變數型态。需要注意的是在NoahWeb中要指定字符串給字符串變量,要在頭尾加上單引号 (例如: '中國')。
可以使用“ADD”運算符将多個字符進行連接運算。
表現層示例
示例輸出
NoahWeb示例說明
輸出一個字符。
邏輯層示例
示例說明
設置一個變量名為actiondesc的局部變量的内容為字符"編輯内容"
表現層示例
示例輸出
NoahWeb1.1示例說明
将兩個字符串相加後輸出。
邏輯層示例
示例說明
設置一個變量名為actiondesc的局部變量的内容為字符"編輯内容動作"
類
作用
表示文本,即一系列 Unicode 字符。
命名空間
System
程序集
mscorlib(在 mscorlib.dll 中)
語法
Visual Basic(聲明)C#
[SerializableAttribute][ComVisibleAttribute(true)]publicsealedclassString:IComparable,ICloneable,IConvertible,IComparableC++
[SerializableAttribute][ComVisibleAttribute(true)]publicrefclassStringsealed:IComparable,ICloneable,IConvertible,IComparableJ#
/**@attributeSerializableAttribute()*//**@attributeComVisibleAttribute(true)*/publicfinalclassStringimplementsIComparable,ICloneable,IConvertible,IComparableJScript
SerializableAttributeComVisibleAttribute(true)publicfinalclassStringimplementsIComparable,ICloneable,IConvertible,IComparableXAML
不适用。
C++中
C++中的string類
MFC中的CString類使用起來非常的方便好用,但是如果離開了MFC框架,還有沒有這樣使用起來非常方便的類呢?答案是肯定的。也許有人會說,即使不用MFC框架,也可以想辦法使用MFC中的API,具體的操作方法在本文最後給出操作方法。
其實,可能很多人很可能會忽略掉标準C++中string類的使用。标準C++中提供的string類得功能也是非常強大的,一般都能滿足我們開發項目時使用。現将具體用法的一部分展示如下:
包含
要想使用标準C++中string類,必須要包含如下内容:
#include下面你就可以使用string/wstring了,它們兩分别對應着char和wchar_t。
用法
string和wstring的用法是一樣的,以下隻用string作介紹。
string類的構造函數:string(const char *s); //用c字符串s初始化 string(int n,char c); //用n個字符c初始化
此外,string類還支持默認構造函數和複制構造函數,如string s1;string s2="hello";都是正确的寫法。當構造的string太長而無法表達時會抛出length_error異常 。
string類的字符操作:const char &operator[](int n)const; const char &at(int n)const; char &operator[](int n); char &at(int n);
operator[]和at()均返回當前字符串中第n個字符的位置,但at函數提供範圍檢查,當越界時會抛出out_of_range異常,下标運算符[]不提供檢查訪問。
const char *data()const;//返回一個非null終止的c字符數組 const char *c_str()const;//返回一個以null終止的c字符串
int copy(char *s, int n, int pos = 0) const;//把當前串中以pos開始的n個字符拷貝到以s為起始位置的字符數組中,返回實際拷貝的數目
完整特性
詳細講解請看cplusplus:
string的特性描述:int capacity()const; //返回當前容量(即string中不必增加内存即可存放的元素個數)int max_size()const; //返回string對象中可存放的最大字符串的長度int size()const; //返回當前字符串的大小int length()const; //返回當前字符串的長度 bool empty()const; //當前字符串是否為空 void resize(int len,char c);//把字符串當前大小置為len,并用字符c填充不足的部分string類的輸入輸出操作:string類重載運算符operator>>用于輸入,同樣重載運算符operator<<用于輸出操作。 函數getline(istream &in,string &s);用于從輸入流in中讀取字符串到s中,以換行符'n'分開。
string的賦值:string &operator=(const string &s);//把字符串s賦給當前字符串string &assign(const char *s);//用c類型字符串s賦值string &assign(const char *s,int n);//用c字符串s開始的n個字符賦值string &assign(const string &s);//把字符串s賦給當前字符串string &assign(int n,char c);//用n個字符c賦值給當前字符串string &assign(const string &s,int start,int n);//把字符串s中從start開始的n個字符賦給當前字符string &assign(const_iterator first,const_itertor last); //把first和last叠代器之間的部分賦給字符串string的連接:string &operator+=(const string &s);//把字符串s連接到當前字符串的結尾string &append(const char *s); //把c類型字符串s連接到當前字符串結尾string &append(const char *s,int n);//把c類型字符串s的前n個字符連接到當前字符串結尾string &append(const string &s); //同operator+=()string &append(const string &s,int pos,int n);//把字符串s中從pos開始的n個字符連接到當前字符串的結尾string &append(int n,char c); //在當前字符串結尾添加n個字符cstring &append(const_iterator first,const_iterator last);//把叠代器first和last之間的部分連接到當前字符串的結尾string的比較:bool operator==(const string &s1,const string &s2)const;//比較兩個字符串是否相等 運算符">","<",">=","<=","!="均被重載用于字符串的比較;int compare(const string &s) const;//比較當前字符串和s的大小int compare(int pos, int n,const string &s)const;//比較當前字符串從pos開始的n個字符組成的字符串與s的大小int compare(int pos, int n,const string &s,int pos2,int n2)const;//比較當前字符串從pos開始的n個字符組成的字符串與s中//pos2開始的n2個字符組成的字符串的大小int compare(const char *s) const;int compare(int pos, int n,const char *s) const;int compare(int pos, int n,const char *s, int pos2) const;//compare函數在大于(>)時返回1,小于(<)時返回-1,等于(==)時返回0string的子串:string substr(int pos = 0,int n = npos) const;//返回pos開始的n個字符組成的字符串string的交換:void swap(string &s2); //交換當前字符串與s2的值string類的查找函數:int find(char c, int pos = 0) const;//從pos開始查找字符c在當前字符串的位置int find(const char *s,int pos = 0) const;//從pos開始查找字符串s在當前串中的位置int find(const char *s, int pos, int n) const;//從pos開始查找字符串s中前n個字符在當前串中的位置int find(const string &s,int pos = 0) const;//從pos開始查找字符串s在當前串中的位置 //查找成功時返回所在位置,失敗返回string::npos的值int rfind(char c, int pos = npos) const;//從pos開始從後向前查找字符c在當前串中的位置int rfind(const char *s, int pos = npos) const;int rfind(const char *s, int pos, int n = npos) const;int rfind(const string &s,int pos = npos) const; //從pos開始從後向前查找字符串s中前n個字符組成的字符串在當前串中的位置,成功返回所在位置,失敗時返回string::npos的值int find_first_of(char c, int pos = 0) const;//從pos開始查找字符c第一次出現的位置int find_first_of(const char *s, int pos = 0) const;int find_first_of(const char *s, int pos, int n) const;int find_first_of(const string &s,int pos = 0) const; //從pos開始查找當前串中第一個在s的前n個字符組成的數組裡的字符的位置。查找失敗返回string::nposint find_first_not_of(char c, int pos = 0) const;int find_first_not_of(const char *s, int pos = 0) const;int find_first_not_of(const char *s, int pos,int n) const;int find_first_not_of(const string &s,int pos = 0) const; //從當前串中查找第一個不在串s中的字符出現的位置,失敗返回string::nposint find_last_of(char c, int pos = npos) const;int find_last_of(const char *s, int pos = npos) const;int find_last_of(const char *s, int pos, int n = npos) const;int find_last_of(const string &s,int pos = npos) const;int find_last_not_of(char c, int pos = npos) const;int find_last_not_of(const char *s, int pos = npos) const;int find_last_not_of(const char *s, int pos, int n) const;int find_last_not_of(const string &s,int pos = npos) const; //find_last_of和find_last_not_of與find_first_of和find_first_not_of相似,隻不過是從後向前查找。string類的替換函數:string &replace(int p0, int n0,const char *s);//删除從p0開始的n0個字符,然後在p0處插入串sstring &replace(int p0, int n0,const char *s, int n);//删除p0開始的n0個字符,然後在p0處插入字符串s的前n個字符string &replace(int p0, int n0,const string &s);//删除從p0開始的n0個字符,然後在p0處插入串sstring &replace(int p0, int n0,const string &s, int pos, int n);//删除p0開始的n0個字符,然後在p0處插入串s中從pos開始的n個字符string &replace(int p0, int n0,int n, char c);//删除p0開始的n0個字符,然後在p0處插入n個字符cstring &replace(iterator first0, iterator last0,const char *s);//把[first0,last0)之間的部分替換為字符串sstring &replace(iterator first0, iterator last0,const char *s, int n);//把[first0,last0)之間的部分替換為s的前n個字符。string &replace(iterator first0, iterator last0,const string &s);//把[first0,last0)之間的部分替換為串sstring &replace(iterator first0, iterator last0,int n, char c);//把[first0,last0)之間的部分替換為n個字符cstring &replace(iterator first0, iterator last0,const_iterator first, const_iterator last);//把[first0,last0)之間的部分替換成[first,last)之間的字符串。string類的插入函數:string &insert(int p0, const char *s);string &insert(int p0, const char *s, int n);string &insert(int p0,const string &s);string &insert(int p0,const string &s, int pos, int n); //前4個函數在p0位置插入字符串s中pos開始的前n個字符string &insert(int p0, int n, char c);//此函數在p0處插入n個字符citerator insert(iterator it, char c);//在it處插入字符c,返回插入後叠代器的位置void insert(iterator it, const_iterator first, const_iterator last);//在it處插入[first,last)之間的字符void insert(iterator it, int n, char c);//在it處插入n個字符cstring類的删除函數iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last);//删除[first,last)之間的所有字符,返回删除後叠代器的位置。iterator erase(iterator it);//删除it指向的字符,返回删除後叠代器的位置。string &erase(int pos = 0, int n = npos);//删除pos開始的n個字符,返回修改後的字符串。string類的叠代器處理:string類提供了向前和向後遍曆的叠代器iterator,叠代器提供了訪問各個字符的語法,類似于指針操作,叠代器不檢查範圍。
用string::iterator或string::const_iterator聲明叠代器變量,const_iterator不允許改變叠代的内容。常用叠代器函數有:
const_iterator begin()const; iterator begin(); //返回string的起始位置 const_iterator end()const; iterator end(); //返回string的最後一個字符後面的位置 const_iterator rbegin()const; iterator rbegin(); //返回string的最後一個字符的位置 const_iterator rend()const; iterator rend(); //返回string第一個字符位置的前面rbegin和rend用于從後向前的叠代訪問,通過設置叠代器string::reverse_iterator或string::const_reverse_iterator實現
字符串流處理:通過定義ostringstream和istringstream變量實現,在#include例如:
string input("hello,this is a test"); istringstream is(input); string s1,s2,s3,s4;is>>s1>>s2>>s3>>s4;//s1="hello,this",s2="is",s3="a",s4="test" ostringstream os; os<以上就是對C++ string類的一個簡要介紹。用的好的話它所具有的功能不會比MFC中的CString類遜色多少。
MFC CString
最後要介紹如何在Win32 應用程序中引用MFC中的部分類,例如CString。
1.在工程目錄下右鍵選擇
"Properties”--->"Configuration Properties”--->“General”--->"Use of MFC"--->"Use MFC in a Static Library",
默認的是:"Use Standard Windows Libraries",如下圖1所示:
2.在你所用的所有頭文件之前包含#include
例如:可以在stdafx.h文件的最前面包含#include
語系沿革備注
String 對象稱為不可變的(隻讀),因為一旦創建了該對象,就不能修改該對象的值。看來似乎修改了 String 對象的方法實際上是返回一個包含修改内容的新 String 對象。如果需要修改字符串對象的實際内容,請使用 System.Text.StringBuilder 類。
字符串中的每個 Unicode 字符都是由 Unicode 标量值定義的,Unicode 标量值也稱為 Unicode 碼位或者 Unicode 字符的序号(數字)值。每個碼位都是使用 UTF-16 編碼進行編碼的,編碼的每個元素的數值都用一個 Char 對象表示。
一個 Char 對象通常表示一個碼位,即:Char 的數值等于該碼位。但是,一個碼位可能需要多個編碼元素。例如,Unicode 輔助碼位(代理項對)使用兩個 Char 對象來編碼。
索引
索引是 Char 對象在 String 中的位置,而不是 Unicode 字符的位置。索引是從零開始、從字符串的起始位置(其索引為零)計起的非負數字。連續的索引值可能并不與連續的 Unicode 字符相對應,這是因為一個 Unicode 字符可能會編碼為多個 Char 對象。若要使用每個 Unicode 字符而不是每個 Char 對象,請使用 System.Globalization.StringInfo 類。
序号運算
String 類的成員對 String 對象執行序号運算或語義運算。序号運算是對每個 Char 對象的數值執行的。語義運算則對考慮了特定于區域性的大小寫、排序、格式化和語法分析規則的 String 的值執行。語義運算在顯式聲明的區域性或者隐式當前區域性的上下文中執行。有關當前區域性的更多信息,請參見 CultureInfo.CurrentCulture 主題。
大小寫規則決定如何更改 Unicode 字符的大小寫,例如,從小寫變為大寫。
格式化規則決定如何将值轉換為它的字符串表示形式,而語法分析規則則确定如何将字符串表示形式轉換為值。
排序規則确定 Unicode 字符的字母順序,以及兩個字符串如何互相比較。例如,Compare 方法執行語義比較,而 CompareOrdinal 方法執行序号比較。因此,如果當前的區域性為美國英語,則 Compare 方法認為“a”小于“A”,而 CompareOrdinal 方法會認為“a”大于“A”。
.NET Framework 支持單詞、字符串和序号排序規則。單詞排序會執行區分區域性的字符串比較,在這種比較中,某些非字母數字 Unicode 字符可能會具有特殊的權重。例如,連字符(“-”)的權重非常小,因此“coop”和“co-op”在排序列表中是緊挨着出現的。字符串排序與單詞排序相似,隻是所有非字母數字符号均排在所有字母數字 Unicode 字符前面,沒有特例。
區分運算
區分區域性的比較是顯式或隐式使用 CultureInfo 對象的任何比較,包括由 CultureInfo.InvariantCulture 屬性指定的固定區域性。當前隐式區域性由 Thread.CurrentCulture 屬性指定。
序号排序基于字符串中每個 Char 對象的數值對字符串進行比較。序号比較自動區分大小寫,因為字符的小寫和大寫版本有着不同的碼位。但是,如果大小寫在應用程序中并不重要,則可以指定忽略大小寫的序号比較。這相當于使用固定區域性将字符串轉換為大寫,然後對結果執行序号比較。
區分區域性的比較通常适用于排序,而序号比較則不适合。序号比較通常适用于确定兩個字符串是否相等(即,确定标識),而區分區域性的比較則不适用。
比較和搜索方法的“備注”指定方法是區分大小寫、區分區域性還是兩者區分。根據定義,任何字符串(包括空字符串 (""))的比較結果都大于空引用;兩個空引用的比較結果為相等。
某些 Unicode 字符具有多個等效的二進制表示形式,這些表示形式中包含幾組組合的和/或複合的 Unicode 字符。Unicode 标準定義了一個稱為規範化的過程,此過程将一個字符的任何一種等價二進制表示形式轉換為統一的二進制表示形式。可使用多種遵循不同規則的算法執行規範化,這些算法也稱為範式。.NET Framework 當前支持範式 C、D、KC 和 KD。通常用序号比較來評估一對規範化的字符串。
安全注意事項
如果應用程序進行有關符号标識符(如文件名或命名管道)或持久數據(如 XML 文件中基于文本的數據)的安全決策,則該操作應該使用序号比較而不是區分區域性的比較。這是因為根據起作用的區域性的不同,區分區域性的比較可産生不同的結果,而序号比較則僅依賴于所比較字符的二進制值。
功能
String 類提供的成員執行以下操作:比較 String 對象;返回 String 對象内字符或字符串的索引;複制 String 對象的值;分隔字符串或組合字符串;修改字符串的值;将數字、日期和時間或枚舉值的格式設置為字符串;對字符串進行規範化。
使用 Compare、CompareOrdinal、CompareTo、Equals、EndsWith 和 StartsWith 方法進行比較。
使用 IndexOf、IndexOfAny、LastIndexOf 和 LastIndexOfAny 方法可獲取字符串中子字符串或 Unicode 字符的索引。
使用 Copy 和 CopyTo 可将字符串或子字符串複制到另一個字符串或 Char 類型的數組。
使用 Substring 和 Split 方法可通過原始字符串的組成部分創建一個或多個新字符串;使用 Concat 和 Join 方法可通過一個或多個子字符串創建新字符串。
使用 Insert、Replace、Remove、PadLeft、PadRight、Trim、TrimEnd 和 TrimStart 可修改字符串的全部或部分。
使用 ToLower、ToLowerInvariant、ToUpper 和 ToUpperInvariant 方法可更改字符串中 Unicode 字符的大小寫。
使用 Length 屬性可獲取字符串中 Char 對象的數量;使用 Chars 屬性可訪問字符串中實際的 Char 對象。
使用 IsNormalized 方法可測試某個字符串是否已規範化為特定的範式。使用 Normalize 方法可創建規範化為特定範式的字符串。
獲取字符
string 類型通過下标操作符([ ])來訪問 string 對象中的單個字符。下标操作符需要取一個 size_type 類型的值,來标明要訪問字符的位置。這個下标中的值通常被稱為“下标”或“索引”(index).
可用下标操作符分别取出 string 對象的每個字符,分行輸出:
string str("some string");for (string::size_type ix = 0; ix != str.size(); ++ix)cout << str[ix] << endl;
每次通過循環,就從 str 對象中讀取下一個字符,輸出該字符并換行。
實現的接口
String 類分别用于實現 IComparable、ICloneable、IConvertible、IEnumerable 和 IComparable 接口。使用 Convert 類進行轉換,而不是使用此類型的 IConvertible 顯式接口成員實現。
繼承層次結構
System.Object
System.String
版本信息
.NET Framework
受以下版本支持:3.0、2.0、1.1、1.0
.NET Compact Framework
受以下版本支持:2.0、1.0
XNA Framework
受以下版本支持:1.0